Introduction to Circular Economy
The circular economy is a transformative approach to economic development that aims to minimize waste and make the most of available resources. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a “take, make, dispose” model, the circular economy focuses on recycling, reusing, and repairing products to extend their lifecycle. This sustainable model promotes the continuous use of resources, reduces environmental impact, and fosters innovation in product design and business practices.
In this article, we will explore what a circular economy is, its core principles, its importance, and how businesses and individuals can transition toward a more sustainable future through circular economy practices.
What is a Circular Economy?
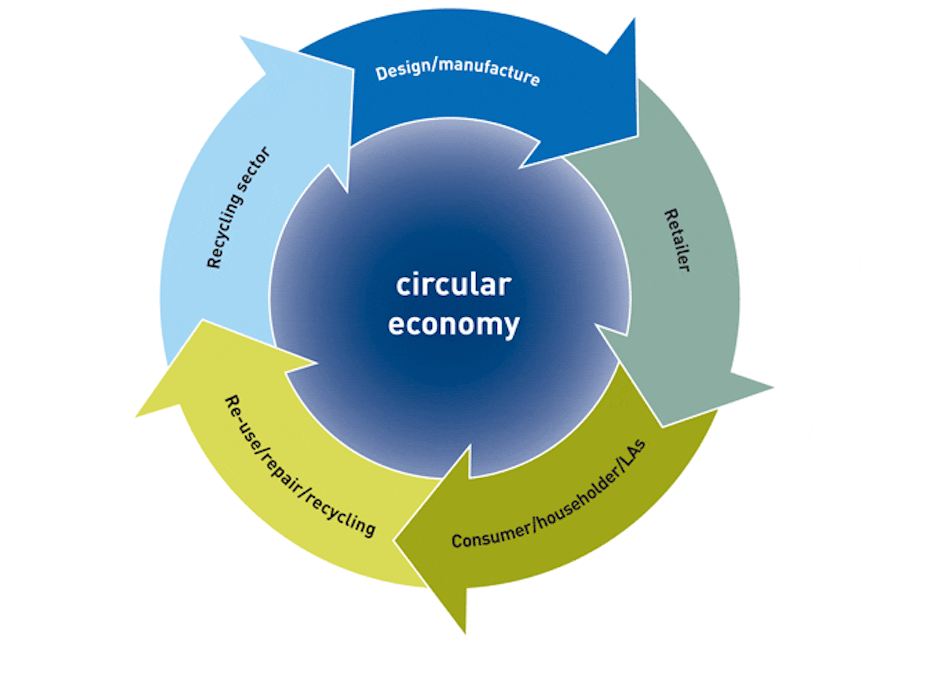
At its core, the circular economy is an economic system that aims to close the loop of product lifecycles. The goal is to reduce waste, conserve resources, and create a regenerative system that benefits both the environment and society. In a circular economy, products are designed with their entire lifecycle in mind, from the raw materials used to the end of their life. Instead of products being discarded, they are reused, refurbished, remanufactured, or recycled into new products, reducing the need for virgin materials and minimizing environmental impact.
The circular economy encourages businesses and individuals to move away from the traditional “take-make-dispose” model and adopt sustainable practices that promote resource efficiency, waste reduction, and economic regeneration.
Core Principles of Circular Economy
A circular economy is based on several key principles that help reshape how we design, produce, and consume goods. These principles include:
-
Design for Longevity
- Products should be designed with durability, repairability, and upgradeability in mind. Instead of being built to fail after a certain period, products in a circular economy are meant to last longer and be easily repaired or modified.
-
Maintain the Value of Products, Materials, and Resources
- Products, components, and materials should be kept in use for as long as possible. This can be achieved through processes like repairing, refurbishing, remanufacturing, or recycling products rather than discarding them.
-
Close the Loop of Product Lifecycles
- The circular economy seeks to create a closed-loop system where waste is minimized, and products or materials are continually reused. This is achieved through practices like recycling, upcycling, and sharing, where the output of one process becomes the input for another.
-
Promote Sharing and Collaboration
- Sharing products or services, rather than owning them outright, can help maximize their utility and reduce overall consumption. Examples include product rental services, sharing platforms (e.g., car-sharing), and collaborative consumption models.
-
Regenerative Design
- Circular economy systems should also be regenerative by design, meaning they restore, renew, or revitalize their sources of energy and materials. For instance, products made from renewable or biodegradable materials are more aligned with https://roman business.com/ principles.
The Importance of a Circular Economy
The circular economy is crucial for several reasons, particularly as the world faces growing challenges related to environmental sustainability, resource depletion, and climate change. Here are some of the key reasons why a circular economy is important:
-
Reducing Waste and Pollution
- One of the primary benefits of the circular economy is the reduction of waste. In a circular model, products are reused, repaired, or recycled, which helps divert waste from landfills and reduces pollution. The approach also minimizes the extraction of raw materials, leading to less environmental degradation.
-
Conserving Natural Resources
- The circular economy helps conserve valuable natural resources by encouraging the reuse and recycling of materials. This reduces the pressure on ecosystems caused by mining, logging, and other resource-extraction industries. By designing products that last longer and are easier to repair, we reduce the need for new materials.
-
Supporting Sustainable Economic Growth
- Rather than relying on finite resources, the circular economy fosters sustainable economic growth by creating new business opportunities in the fields of recycling, refurbishment, and remanufacturing. It promotes a shift from a growth model based on resource extraction to one based on value retention and regeneration.
-
Fighting Climate Change
- By reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing energy-intensive processes, the circular economy can contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions and environmental pollution. The model encourages the use of renewable energy, cleaner manufacturing processes, and sustainable product design, all of which help mitigate the effects of climate change.
-
Creating Jobs and Innovation
- The transition to a circular economy can stimulate job creation, particularly in areas such as repair, remanufacturing, recycling, and product design. It also encourages innovation, as businesses look for new ways to optimize resources and minimize waste.
Examples of Circular Economy in Practice
There are many successful examples of circular economy principles being applied across different industries. Here are a few notable examples:
-
Patagonia
- The outdoor clothing company Patagonia is a leader in sustainability and circular practices. They offer a Worn Wear program, where customers can buy, sell, and trade used Patagonia gear. They also promote product repair services to extend the life of their clothing and ensure that items are not prematurely discarded.
-
Interface
- Interface, a global carpet tile manufacturer, has embraced circular economy practices by using recycled materials and designing products that can be easily taken apart and recycled again. The company aims to achieve a zero-waste model by minimizing its environmental footprint and reusing resources.
-
IKEA
- IKEA has made strides in implementing circular economy principles in its operations. The company offers a take-back service for old furniture in some regions, and its products are increasingly designed with materials that can be recycled or reused. IKEA is also exploring new business models, such as furniture leasing, to promote circularity.
-
TerraCycle
- TerraCycle is a company dedicated to recycling hard-to-recycle materials, such as cigarette butts, chip bags, and toothbrushes. They work with both consumers and businesses to create circular systems for materials that would otherwise end up in landfills.
How Businesses Can Transition to a Circular Economy
For businesses looking to transition to a circular economy, there are several steps that can be taken:
-
Design for Circularity
- Businesses should design products with longevity in mind, ensuring that they can be easily repaired, disassembled, or recycled. This may involve using materials that are more durable, biodegradable, or recyclable.
-
Implement Take-Back Programs
- Offering customers the option to return or exchange used products for reuse or recycling is a key circular economy practice. Businesses can create incentives, such as discounts or loyalty points, to encourage participation in these programs.
-
Collaborate with Other Organizations
- Collaboration is vital in a circular economy. Companies can partner with suppliers, customers, and other organizations to share resources, knowledge, and infrastructure for recycling, repurposing, or remanufacturing.
-
Optimize Resource Efficiency
- Businesses can improve their resource efficiency by reducing waste and energy consumption in their operations. This can be achieved through smarter production methods, waste-to-energy technologies, and using recycled materials in manufacturing processes.
-
Educate Consumers
- Encouraging consumers to adopt circular behaviors, such as repairing products instead of discarding them or purchasing second-hand items, is essential for a circular economy to thrive. Businesses can provide information about the environmental benefits of circular practices and offer incentives for participation.
Challenges in Adopting Circular Economy
Despite the many benefits, transitioning to a circular economy comes with challenges:
-
Initial Costs
- Shifting to a circular model often requires upfront investment in new technologies, processes, or redesigning products. For some businesses, this initial investment may seem prohibitive.
-
Consumer Awareness
- Changing consumer behavior to embrace circular practices, such as product repair, reuse, or recycling, can be a challenge. Raising awareness and making circular options convenient is essential for increasing participation.
-
Supply Chain Adjustments
- Businesses may need to rework their entire supply chain to ensure that materials are sourced sustainably and products can be easily recycled or remanufactured. This can require significant changes in how materials are sourced and products are distributed.
Conclusion: The Future of the Circular Economy
The circular economy represents a powerful and necessary shift toward a more sustainable and regenerative economic model. By focusing on the continuous use of resources, reducing waste, and fostering innovation, the circular economy offers a solution to many of the environmental and economic challenges we face today.
As more businesses and individuals embrace circular practices, we move closer to a future where waste is minimized, resources are used more efficiently, and environmental impact is drastically reduced. The circular economy is not just a concept for the future; it’s a practical, sustainable model for today that can revolutionize how we produce, consume, and live.